Step 4. Fully automatic static routing table configuration¶
Goals¶
Just as with IP addresses, in many cases, the configurator sets up routes in a network properly without any user input. This step demonstrates the default configuration for routing.
The model¶
This step uses the same network as the previous steps, ConfiguratorA. The configuration for this step in omnetpp.ini is the following:
[Config Step4]
sim-time-limit = 500s
network = ConfiguratorA
description = "Fully automatic static routing table configuration"
*.host1.numApps = 1
*.host1.app[0].typename = "PingApp"
*.host1.app[0].destAddr = "host7"
*.visualizer.routingTableVisualizer.displayRoutingTables = true
*.visualizer.routingTableVisualizer.destinationFilter = "host7"
The configuration leaves the configurator’s parameters at their defaults. The configurator’s parameters concerning static routing are the following:
addStaticRoutes = default(true): This is the main switch that turns on automatically filling routing tables. When this setting is turned off, only routes specified in the XML configuration are added, and all the following parameters are ignored.addDefaultRoutes = default(true): Add a default route if all routes from a node go through the same gateway. This is often the case with hosts, which usually connect to a network via a single interface.addSubnetRoutes = default(true): Optimize routing tables by adding routes towards subnets instead of individual interfaces.optimizeRoutes = default(true): Optimize routing tables by merging entries where possible.
Adding traffic¶
We add some traffic to the network so that we can see which way packets are routed. We use ping applications for this purpose throughout the tutorial.
In this step, we configure host1 to ping host7 in order to see
the route between the two hosts.
Logging and visualization settings¶
The RoutingTableCanvasVisualizer module (present in the network as a
submodule of IntegratedCanvasVisualizer) can be used to visualize IP
routes in the network. Routes are visualized with arrows. In general, an
arrow indicates an entry in the source host’s routing table. It points
to the host that is the next hop or gateway for that routing table
entry. The visualization is activated by setting the
RoutingTableVisualizer’s displayRoutingTables parameter to
true. The set of routes to be visualized is selected with the
visualizer’s destinationFilter and nodeFilter parameters. All
routes leading towards the selected set of destinations from the
selected set of source nodes are indicated by arrows. The default
setting for both parameters is "*", which visualizes all routes
going from every node to every other node. Visualizing routes from all
nodes to all destinations can often make the screen cluttered. In this
step, the destinationFilter is set to visualize all routes heading
towards host7.
The visualizer annotates the arrows with information about the visualized route by default. This feature can be customized and toggled on and off with the visualizer’s parameters (discussed in later steps.)
Additional settings pertaining to routing are specified in the
General configuration in omnetpp.ini:
[General]
description = "(abstract)"
# Configurator settings
*.configurator.dumpAddresses = true
*.configurator.dumpTopology = true
*.configurator.dumpLinks = true
*.configurator.dumpRoutes = true
# Routing settings
*.*.ipv4.arp.typename = "GlobalArp"
*.*.ipv4.routingTable.netmaskRoutes = ""
# Visualizer settings
*.visualizer.interfaceTableVisualizer.displayInterfaceTables = true
*.visualizer.interfaceTableVisualizer.nodeFilter = "not (*switch* or *Switch* or *AP*)"
The dumpTopology, dumpLinks, and dumpRoutes parameters are
set to true. These parameter settings instruct the configurator to
print to the module output the topology of the network, the recognized
network links, and the routing tables of all nodes, respectively.
Topology describes which nodes are connected to which nodes. Hosts that
can directly reach each other (i.e. the next hop is the destination),
are considered to be on the same link.
Additional configuration¶
The General configuration also sets up GlobalArp to keep the
packet exchanges simpler. GlobalArp fills the ARP tables of all
nodes in advance, so when the simulation begins, no ARP exchanges are
necessary.
The **.routingTable.netmaskRoutes = "" line keeps the routing table
modules from adding netmask routes to the routing tables. Netmask routes
mean that nodes with the same netmask but different IP addresses should
reach each other directly. These routes are also added by the
configurator, so netmaskRoutes is turned off to avoid duplicate
routes.
Results¶
The visualized routes are displayed on the following image:
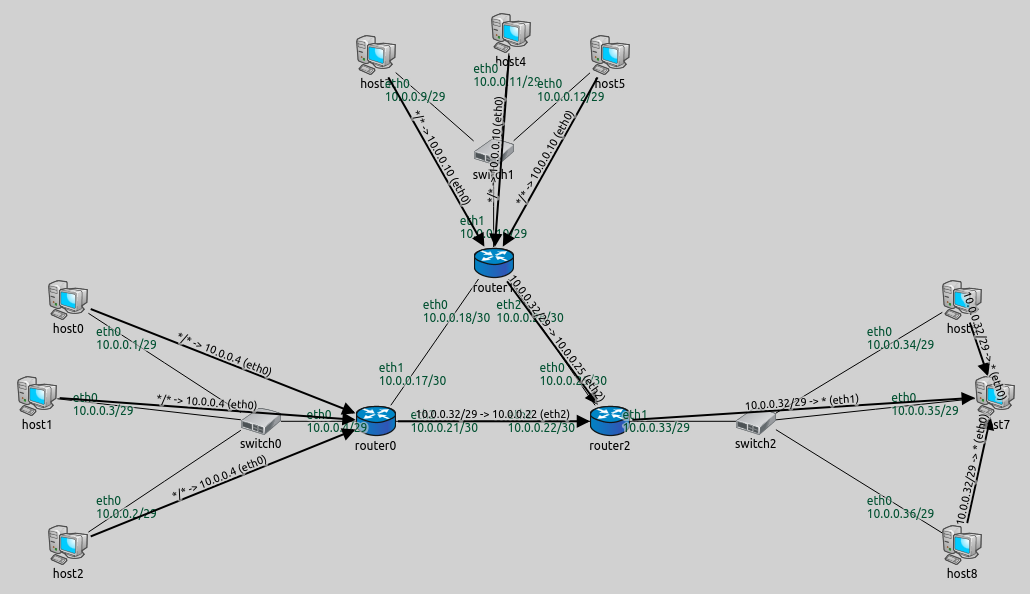
Routes from all nodes to host7 are visualized. Note that arrows
don’t go through switches, because they are not the next hop. When
routes are concerned, switches are transparent L2 devices.
The routing tables are the following (routes visualized on the image above are highlighted):
Node ConfiguratorB.host0 (hosts 1-2 are similar)
-- Routing table --
Destination Netmask Gateway Iface Metric
10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 * eth0 (10.0.0.1) 0
* * 10.0.0.4 eth0 (10.0.0.1) 0
Node ConfiguratorB.host3 (hosts 4-5 are similar)
-- Routing table --
Destination Netmask Gateway Iface Metric
10.0.0.8 255.255.255.248 * eth0 (10.0.0.9) 0
* * 10.0.0.10 eth0 (10.0.0.9) 0
Node ConfiguratorB.host6 (hosts 7-8 are similar)
-- Routing table --
Destination Netmask Gateway Iface Metric
10.0.0.32 255.255.255.248 * eth0 (10.0.0.34) 0
* * 10.0.0.33 eth0 (10.0.0.34) 0
Node ConfiguratorB.router0
-- Routing table --
Destination Netmask Gateway Iface Metric
10.0.0.18 255.255.255.255 * eth1 (10.0.0.17) 0
10.0.0.22 255.255.255.255 * eth2 (10.0.0.21) 0
10.0.0.25 255.255.255.255 10.0.0.22 eth2 (10.0.0.21) 0
10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 * eth0 (10.0.0.4) 0
10.0.0.32 255.255.255.248 10.0.0.22 eth2 (10.0.0.21) 0
10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 10.0.0.18 eth1 (10.0.0.17) 0
Node ConfiguratorB.router1
-- Routing table --
Destination Netmask Gateway Iface Metric
10.0.0.17 255.255.255.255 * eth0 (10.0.0.18) 0
10.0.0.22 255.255.255.255 10.0.0.25 eth2 (10.0.0.26) 0
10.0.0.25 255.255.255.255 * eth2 (10.0.0.26) 0
10.0.0.8 255.255.255.248 * eth1 (10.0.0.10) 0
10.0.0.32 255.255.255.248 10.0.0.25 eth2 (10.0.0.26) 0
10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 10.0.0.17 eth0 (10.0.0.18) 0
Node ConfiguratorB.router2
-- Routing table --
Destination Netmask Gateway Iface Metric
10.0.0.18 255.255.255.255 10.0.0.26 eth0 (10.0.0.25) 0
10.0.0.21 255.255.255.255 * eth2 (10.0.0.22) 0
10.0.0.26 255.255.255.255 * eth0 (10.0.0.25) 0
10.0.0.8 255.255.255.248 10.0.0.26 eth0 (10.0.0.25) 0
10.0.0.32 255.255.255.248 * eth1 (10.0.0.33) 0
10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 10.0.0.21 eth2 (10.0.0.22) 0
The * for the gateway means that the gateway is the same as the destination. Hosts have a routing table entry to reach other nodes on the same subnet directly. They also have a default route with the router as the gateway for packets sent to outside-of-subnet addresses. Routers have three rules in their routing tables for reaching the other routers, specifically, those interfaces of the other routers that are not facing the hosts.
Below is a video of host1 pinging host7.
Sources: omnetpp.ini,
ConfiguratorA.ned
Discussion¶
Use this page in the GitHub issue tracker for commenting on this tutorial.